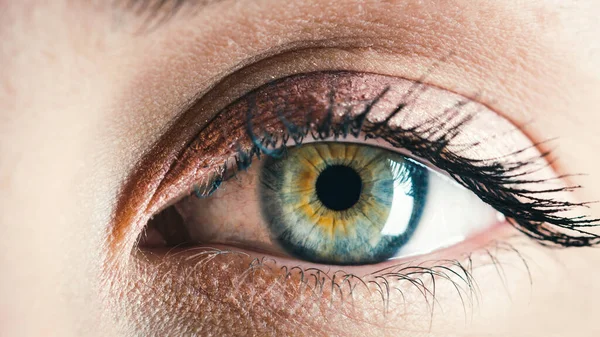
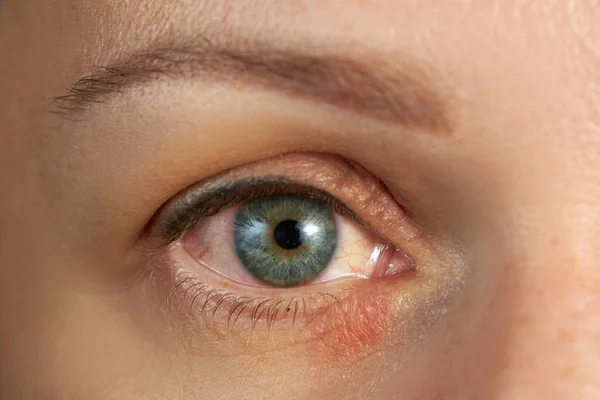
How Eyes infections is damage our skin includes the risk of spreading infection from the eye area to the surrounding skin, leading to irritation, redness, and potentially more severe skin issues.
Eye infections, often dismissed as mere inconveniences, can have surprisingly far-reaching effects on our skin. When left untreated or poorly managed, these infections can disrupt the delicate balance of our facial skin, leading to inflammation, irritation, and even long-term damage.
From the spread of bacterial or viral agents to the impact of constant rubbing or scratching, eye infections can compromise our skin’s health in ways that go beyond the immediate discomfort. Understanding these connections is crucial for maintaining not only eye health but also the integrity of our skin.
Dive into the intricate relationship between eye infections and skin damage to uncover how these seemingly isolated issues can intersect and what steps you can take to safeguard both your eyes and skin.

How Eyes Infection Is Damage Our SKin
Eye infections, whether bacterial, viral, or fungal, can have unexpected impacts on our skin, particularly around the eye area. These infections can cause irritation, inflammation, and swelling, leading to visible skin damage. Understanding how eye infections affect the skin is crucial for effective prevention and treatment.
In this article, we’ll explore the connection between eye infections and skin damage, highlighting common issues and preventive measures.
The Connection Between Eye Infections and Skin Health
Eye infections, including conjunctivitis (pink eye), blepharitis, and styes, often lead to inflammation and irritation in and around the eyes. This inflammation can extend to the delicate skin surrounding the eyes, causing redness, swelling, and discomfort.
Bacterial infections can result in crusting and discharge, which can further irritate the skin. Viral infections, such as those caused by herpes simplex, can lead to more severe skin issues, including sores and lesions. Understanding these connections is essential for managing symptoms and protecting the skin.
Common Skin Reactions to Eye Infections
When dealing with an eye infection, the skin around the eyes can exhibit several reactions. Redness and swelling are the most common symptoms, resulting from increased blood flow and immune response in the area. This can cause the skin to look puffy and irritated.
Additionally, prolonged rubbing of the eyes due to itching or discomfort can exacerbate skin damage, leading to potential dark circles and even skin infections. These skin reactions are not just cosmetic but can also indicate the severity of the eye infection.
Preventing Skin Damage from Eye Infections
To prevent skin damage from eye infections, maintaining good hygiene is crucial. Avoid touching or rubbing the eyes, as this can spread infection and worsen skin irritation.
Use clean towels and tissues, and wash hands frequently. Applying a cold compress can help reduce swelling and soothe irritated skin. For bacterial infections, following prescribed treatments and avoiding the use of shared makeup or eye products is essential.
In cases of viral infections, avoiding direct contact and using antiviral medications as directed can prevent further skin complications.
Treating Skin Damage from Eye Infections
Treating skin damage caused by eye infections involves addressing both the infection and its impact on the skin. For mild irritation, gentle cleansers and moisturizers can help soothe the affected area. Avoid using harsh skincare products that may further irritate the skin.
If the infection leads to more severe skin damage, such as sores or persistent redness, consulting a dermatologist is advisable. They can provide targeted treatments to heal the skin and prevent long-term damage.
Additionally, proper treatment of the underlying eye infection is crucial to ensure complete recovery and prevent recurrence.
In summary, eye infections can significantly impact the skin around the eyes, causing redness, swelling, and irritation. By understanding these effects and taking preventive measures, you can minimize skin damage and promote healing. Always consult healthcare professionals for effective treatment and care.
Types of Eye Infections and Their Characteristics
Eye infections can cause discomfort and affect vision. Here are the common types:
Conjunctivitis (Pink Eye)
Conjunctivitis, or pink eye, is caused by bacteria, viruses, or allergens. Bacterial conjunctivitis results in a yellowish-green discharge, while viral conjunctivitis is often linked to colds and spreads easily. Allergic conjunctivitis is triggered by pollen or dust.
Symptoms
Key symptoms include redness, itching, and discharge. The eye may feel gritty or sandy. Pink eye can be highly contagious and spread through contact with contaminated hands or objects.
Blepharitis
Blepharitis is primarily due to bacterial infections or meibomian gland dysfunction. This condition affects the eyelid margins where the eyelashes grow. It can result from seborrheic dermatitis or other skin conditions.
Symptoms
The main symptoms are inflammation of the eyelids and crusting at the base of the eyelashes. Blepharitis can cause the eyelids to feel sore and swollen, and may lead to a dry, irritated feeling.
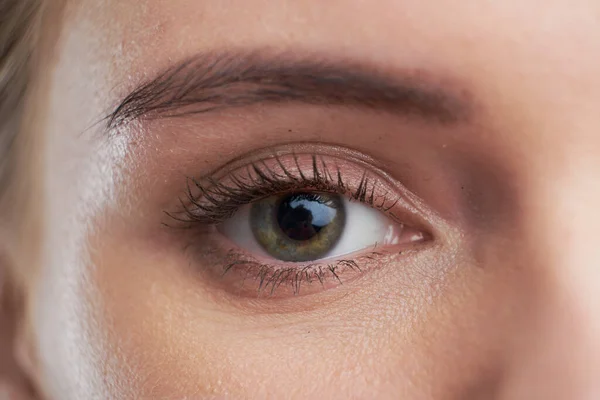
Mechanisms of Skin Damage
Infections can spread from one part of the skin to another through direct contact. Bacteria and viruses often move from the eye area to surrounding skin, especially if the area is touched frequently.
For instance, conjunctivitis, commonly known as pink eye, can easily transfer pathogens to nearby facial skin. This direct spread can lead to rashes or additional infections on the face.
Inflammatory Responses
Inflammation plays a crucial role in skin health. When the skin is injured or infected, it responds with inflammation, characterized by redness, swelling, and heat.
Chronic inflammation can damage skin cells and compromise the skin barrier, leading to conditions like eczema or psoriasis. Persistent inflammation can also cause skin to become more sensitive and prone to further issues.
Complications from Scratching and Rubbing
Scratching or rubbing irritated skin can lead to severe complications. Physical contact can worsen existing conditions, like eczema or dermatitis, and increase the risk of secondary infections.
Frequent scratching often breaks the skin, creating entry points for bacteria. This can result in secondary infections, prolonged healing times, and increased skin damage.